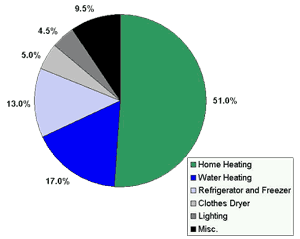
Electricity has no odor and can't be seen, so it is often puzzling where your energy dollar goes!
While consumption patterns vary from home to home, we have some average consumption figures for home electric energy.
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a measure of electric energy consumed over a period of time.
A watt is the amount of energy required to operate the electric device. To calculate the wattage of an appliance, multiply the voltage by the amperage.
These values are typically found on the backside or bottom of the appliance or on the nameplate.
To convert the watts to kilowatts, simply divide by 1000.
Once you know the kilowatt value, multiply by the number of hours of operation to determine the kilowatt-hour consumption.